

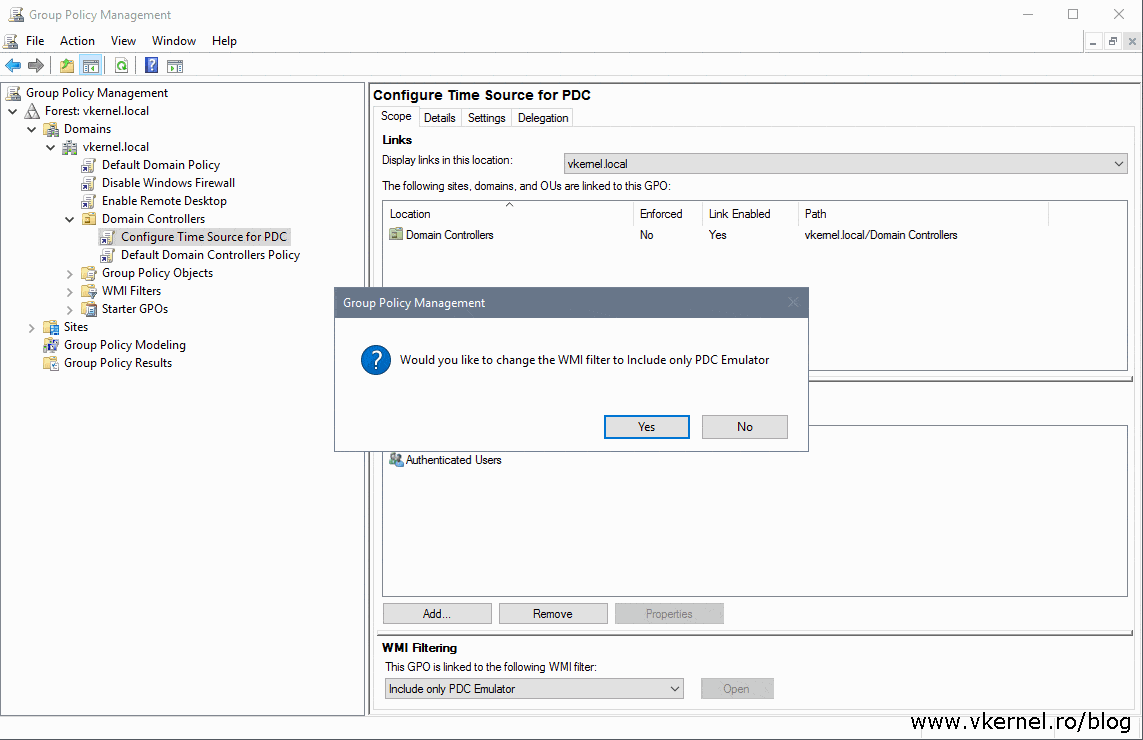
For computers that are not joined to a domain, you can start the time service manually. The W32Time service starts automatically on computers that are joined to a domain. So on the whole, all the systems are uses UTC time, while displaying the system time it will be converted according to the time zone configuration. Understanding the time zone configuration in windowsīefore describing the time zone configuration you should know what is time zone and how and why it’s used, relation between time and time zone, and difference between timeĭue to time difference between the countries, like time in UK is not the same in US, to differentiate the time between the different parts of the world we use the time zone, I call it difference between timeĬomputers and servers store time in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), when viewed through any application (or) viewing system time it’s displayed according to the local time zone of the computer, UTC is equal to GMTĬurrent system time (UTC) + Time zone (UTC +5.30) = Display time Any domain controller that accesses time directly from the PDC emulator of the forest root domain is designated as stratum. The forest root domain can also be called the parent domain, and each domain under the parent or forest root can be called a child domain. The external time source holds the position of greatest accuracy, or stratum one. In Active Directory environment PDC emulator is acting as a time server, PDC emulator is located in the forest root domain and is connected to an external time source. Time synchronization in an Active Directory
Client’s clock time should sync with the server (Domain controllers) clock time in order to get successful authentication The server then acknowledges the client by sending the modified authenticator with the client’s original timestamp back to the client for identification. If the client’s time falls within the allowable skew and its timestamp is unique, the server then slightly modifies the contents of the original authenticator and re-encrypts it with the client’s secret key, establishing mutual authentication. The server then checks the client’s time to make sure that it falls within the server’s time and the allowable skew and client time should be unique not the same as or earlier than the time of another authenticator When the server receives request for authentication (the ticket), it check for client’s clock time. I am not going to explain the Kerberos authentication process, just how the Kerberos uses the time for authentication. Let me explain how the Time and Time sync works.Īctive directory uses the Kerberos for authenticating users and computers in a domain

In the environment where the sites are located in different geographical locations, most of the administrators have confused with time services and how it’s works.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
